
As compared to windows 3.1, windows 95 comes with more built-in capability. They include improved networking, a better kernel, superior multitasking, access to more memory as well as better GUI (graphical user interface).
Anatomy of the Operating System
One of the main job of an operating system is to run applications and
make sure that they function properly. The architeture of Wndows
95 is given below.
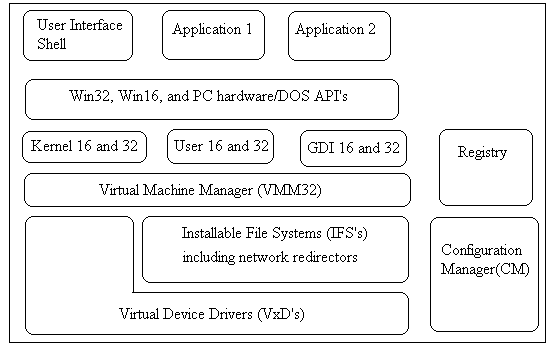
API's under Windows 95
When windows 3.0 was first introduced, it was
adapted to the 286 processor architecture. As the 286 is a 16-bit
processor, the possible set of commands that a program could enter was
called Win16 API. With the introduction of 32-bit processors, Windows
95 contains a newer API known as Win 32 API. Since there are already
thousands of older windows programs in the market that are perfectly functional,
Windows 95 must support these older programs if not nobody will purchase
it. Hence, Windows 95 comes with both Win 16 and Win 32 API as well
as a DOS-compatible API.
Kernel Modules
GDI (Graphical user interface)
The GDI primarily acts as one of the kernel's helper program to take
care of the graphical things in Windows 95. Like the kernel, it exists
in two forms GDI16 and GDI32. whenever you put a bitmap on the screen,
your request is channelled through GDI. Areas under its control include
bitmaps, colour, curcurs, icons,fontsand graphical objects.
User 16 and 32
The user interaction with the window boxs such as clicking a button,
choosing from list boxs, and so on are handled by the User module.
As before it contains both a 16-bit and a 32-bit module.
Virtual Machine Manager (VMM32)
The VMM32 manages memory and provides support to the management of
virtual memory. It multitask DOS programs by creating multiple virtual
PCs(vrtual machines) and they exploit a feature know as page mapping.
As an example, suppose a computer system has 32MB of memory. The
VMM32 can allocate memory from 10MB to 11MB to a DOS program. Therefore
the DOS program only sees 1MB of memory. Whenever the DOS program
tried to access memory let say memory location 600, the VMM32 will automatically
map the memory adress by adding 10MB to the memory location.
Virtual Device Drivers (VxD's)
A progra, communicates with a piece of hardware such as a modem or
graphics card by means of input/output addresses ( I/O addresses).
They are similar to memory addresses except that I/O addresses access I/O
devices instead of memory. A virtual device driver is a program that
the operating system assigns to a particular I/O address. For example,
a application program tries to access I/O address 100 which is assigned
to the mouse driver. Upon accessing the address, the mouse driver
will cme into action, behaving like the original piece of hardware.
Memory Management under Windows
95
Security rings are used to protect memory space of a program so that
they will not be altered by other unauthorised programs. Ring 0 programs
can protect memory in that they can allocate spaces of memory to particular
programs and detect when an illegal program tries to access that particular
block of memory, this invasion is known as a general protection fault,
or a GP fault. Ring 1 programs can also allocate memory but as long
as they do not override a command of ring 0 program. The same theory
applies to the next ring level and so on.
Windows 95 only uses 2 rings, ring 0 and ring 3. Only the
VMM and VxD's are in ring 0 and all the rest are in ring 3.
| A Windows 95 pet trick, try this:
1. Right-click the Desktop, and choose New Folder.
|
| Crashing your machine
1. Open a DOS prompt. (Click on the start button, then programs
and then the MS-DOS prompt)
|